BUSM study shows without immune rejection, potential of differentiated iPS cells in cell
 |
| credit: learn.genetics.utah.edu |

This chart shows star temperatures vs. stellar flux showing various zones including Earth. Credit: Chester Harmon Scientists should ta...
27 Nov 2013 | 1 comments | Read more
Terry Zaperach/NASA, via Agence France-Presse — Getty Images Engineers at a NASA site in Virginia preparing an unmanned craft for its...
01 Sep 2013 | 0 comments | Read more
Scientists from Melbourne IVF and the Royal Women's hospital helped a woman who had both her ovaries removed get pregnant. Australian ...
05 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
Syphilis has become a serious health issue (again) in Latin American countries, with 3 million cases. Every year 330,000 pregnant women w...
03 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
Cardiac stents to open blocked heart arteries and reduce chest pain have been used for decades. However, cardiologists have never been ce...
03 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
A new study on mentholated cigarette use in the U.S. finds an increase in menthol cigarette smoking among young adults and concludes th...
30 Aug 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
Microsoft CEO Steve Ballmer speaks during a press conference on the company's deal with Finnish mobile manufacturer Nokia in Espoo, ...
03 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
Even before Facebook begins displaying splashy video ads, it's preparing for a backlash from users like Amy Pittel. The 44-year...
03 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
Apple will launch its new iPad and iPad mini ahead of the "holiday shopping season," according to a new report. Citing unnamed sources...
13 Aug 2013 | 0 comments| Read more
A new image processing technique automatically calculates where the viewer is located in front of the television. The user can move a...
13 Aug 2013 | 0 comments| Read moreClouds, which can absorb or reflect incoming radiation and affect the amount of radiation escaping from Earth's atmosphere, remain the g...
03 Sep 2013 | 0 comments| Read moreSyria's civil war imperils nation's rich archaeological treasures
Why Do U.S. Behavioral Science Researchers Keep Skewing Their Results?
3D-Printing Not Yet Mainstream, But Critics Are Missing the Point (Op-Ed)
Edinburgh zoo put on 24-hour alert for Tian Tian A Giant Pregnent Panda
Ice Is Disappearing in Greenland-- Heat from Mantle results Ice Melting

The newfound species of walking shark, Hemiscyllium Halmahera, grows up to 27 inches (70 centimeters) long and is harmless to humans. ...
31 Aug 2013 | Read more
In a first-of-its-kind study, a Michigan State University researcher has demonstrated that birds communicate via scents, and that odo...
04 Sep 2013 | Read more
In the computer simulation, the composite is cut (far left) and the nanorods begin migration to the cut interface. In the third image, t...
27 Nov 2013 | Read more
Clouds, which can absorb or reflect incoming radiation and affect the amount of radiation escaping from Earth's atmosphere, remain the g...
03 Sep 2013 | Read more
Mad Science J.J. via Wikimedia Commons Despite its lofty ideals, science isn't always impartial and unbiased. S...
31 Aug 2013 | Read more
From the nature of the universe (that's if there is only one) to the purpose of dreams, there are lots of things we still don't k...
02 Sep 2013 | Read more
Aldric Chang The tradition of anticipating (Western) summertime full-length feature films with the best special effects spectacle fro...
28 Jan 2013 | Read more Syria's civil war imperils nation's rich archaeological treasures
Syria's civil war imperils nation's rich archaeological treasures  Why Do U.S. Behavioral Science Researchers Keep Skewing Their Results?
Why Do U.S. Behavioral Science Researchers Keep Skewing Their Results?  New 'Walking' Shark Species
New 'Walking' Shark Species  3D-Printing Not Yet Mainstream, But Critics Are Missing the Point (Op-Ed)
3D-Printing Not Yet Mainstream, But Critics Are Missing the Point (Op-Ed)  How we create Memories ?
How we create Memories ?  Edinburgh zoo put on 24-hour alert for Tian Tian A Giant Pregnent Panda
Edinburgh zoo put on 24-hour alert for Tian Tian A Giant Pregnent Panda  Have You Watch Mars Align starry Twins on Sunday?
Have You Watch Mars Align starry Twins on Sunday?  A More Nuanced Genetic Code: Rethinking
A More Nuanced Genetic Code: Rethinking  Ice Is Disappearing in Greenland-- Heat from Mantle results Ice Melting
Ice Is Disappearing in Greenland-- Heat from Mantle results Ice Melting 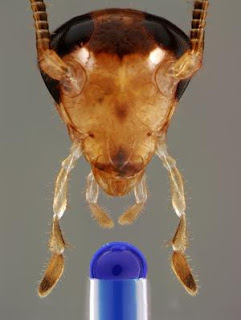 Bittersweet: Bait-averse cockroaches shudder at sugar
Bittersweet: Bait-averse cockroaches shudder at sugar