 |
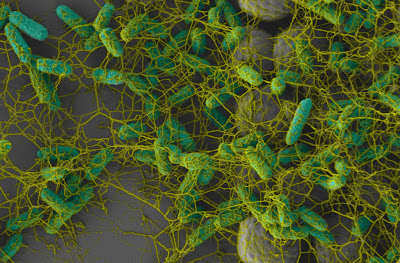
Rather than being repelled by nanostructured surfaces, as materials scientists have hoped, bacteria with many flagella seem to love them. Credit: False-color scanning electron micrograph courtesy of Ronn Friedlander and Michael Bucaro
|
New research from Harvard University helps to explain how waterborne bacteria can colonize rough surfaces -- even those that have been designed to resist water. A team of materials scientists and microbiologists studied the gut bacterium Escherichia coli, which has many flagella that stick out in all directions. The researchers found that these tails can act as biological grappling hooks, reaching far into nanoscale crevices and latching the bacteria in place.
The scourge of the health care industry, bacteria like E. coli are adept at clinging to the materials used in medical implants like pacemakers, prosthetics, stents, and catheters, spreading slimy biofilm and causing dangerous infections. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on March 18, suggest that antibacterial materials should incorporate both structural and chemical deterrents to bacterial attachment.
E. coli are equipped with two types of appendages: pili, which are short, sticky hairs, and the whip-like flagella, which are often twice as long as the bacterium itself. Pili had previously been recognized as playing a critical role in the formation of biofilms. These short hairs, up to only a micron in length in E. coli, can stick to surfaces temporarily, while the bacteria secrete a thick slime that holds them permanently in place.
Flagella, on the other hand, typically play a propulsive role, helping bacteria to swim and steer in liquid environments. As it turns out, though, when it's time to settle in one place, flagella also contribute to adhesion on rough surfaces, where the pili would have access to fewer attachment points.
Nanoscale crevices, such as those deliberately built into superhydrophobic materials, often trap air bubbles at the surface, which initially prevent E. coli from attaching at all. The new research shows that the bacteria can gradually force these bubbles to disperse by, essentially, flailing their arms. Once the cracks and crevices are wet, although the cell bodies can't fit into the gaps, the flagella can reach deep into these areas and attach to a vast amount of new surface area.
"The diversity of strategies and methods by which bacteria can adhere reflects their need to survive in a huge variety of environments," says lead author Ronn S. Friedlander, a doctoral student in the Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology. "Of course, if we could prevent biofilms from forming where we didn't want them to, there would be immense benefits in medicine."
Friedlander studies in the lab of Harvard professor Joanna Aizenberg, who holds a joint appointment as Amy Smith Berylson Professor of Materials Science at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences and as Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology (CCB). Aizenberg's laboratory group has been working to develop extremely slippery surfaces that repel water, dirt, oil, and bacteria.
The surface chemistry of antibacterial materials appears to be just as important as the topography. E. coli flagella have previously been known to adhere to certain proteins on the surface of cells in the gut wall, indicating that the bacteria are capable of bonding with specific molecular matches. But in the 1970s, biologists observing E. coli on microscope slides had also seen something curious: bacteria wheeling about under the coverslip, as if tethered to the glass by a single flagellum. This ability to stick to any surface at all -- termed nonspecific adhesion -- is part of what makes it easy for bacteria to survive on the surface of medical implants.
Rather than having to find a perfect molecular match, the flagella of E. coliappear to cling to surfaces using a combination of many weak bonds.
"The ideal antibacterial material would be topographically patterned with tiny crevices to limit the amount of surface area that was immediately accessible to bacteria via their pili, but also engineered in terms of its surface chemistry to reduce the ability of the flagella to make bonds within those crevices," says Aizenberg. "Surface structuring alone will not achieve this goal."
In 2012, Aizenberg's group demonstrated a material they call SLIPS (for Slippery, Liquid-Infused Porous Surfaces). It was patterned with nanoscale pores, which were filled with a fluorinated lubricant that was shown to prevent biofilms from attaching.
The findings from this line of research are relevant beyond the field of medicine, as biofilms also pose problems for the food industry, water treatment, ship maintenance, and other industries where slime can clog pipes and filters, corrode metal, or cause contamination. But this latest work also helps to explain, on a basic level, how bacteria succeed at colonizing such a wide variety of environments, including the human gut. Having many flagella, the authors note in their paper, "may be particularly important in an intestinal environment coated with microvilli."
In addition to her appointments at Harvard SEAS and CCB, Aizenberg is Director of the Kavli Institute for Bionano Science and Technology at Harvard; a Core Faculty Member at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard; and Director of the Science Programs at the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study; among other roles at the University.
Coauthors included Hera Vlamakis, an instructor in microbiology and molecular genetics at Harvard Medical School; Philseok Kim, a researcher at the Wyss Institute; Mughees Khan, a staff scientist in nanofabrication at the Wyss Institute; and Roberto Kolter, Professor of Microbiology and Immunobiology at Harvard Medical School.
The research was supported in part by the U.S. Office of Naval Research (N00014-11-1-0641), the BASF Advanced Research Initiative at Harvard University, and a National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship. The researchers also benefited from the facilities of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Microsystems Technology Laboratories and the Harvard Center for Nanoscale Systems, a member of the NSF-supported National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network (ECS-0335765).